This is the first part of Ableton live tutorial series.
Electronic music production is in “boom”. Today each and every music producer, even newbie musicians are used to recording their creations on their laptop with only two things – An audio interface and DAW software.
However, In electronic music production, just the knowledge of music is not enough. Without proper knowledge of “How to use a DAW“, we are not going to produce quality music.
Choosing the right DAW is also very important. Not each DAW is perfect in everything.
As you know, “from songwriting to mixing and mastering” there are several stages of music production.
But what you don’t know is that not every DAW is perfect in all tasks. Some are good at mixing/mastering whereas some are good at taking vocals.
Even the music genre plays a big role in choosing a perfect DAW. Like, Protools is perfect for background scoring where Logic Pro X is perfect for Music Programming. As per the reviews, Logic Pro X is great for the Hip-hop music genre.
But there is also a DAW in the market which is literally perfect for all music production stages and genres – Ableton Live.
Disclosure: This post may contain affiliate links, which means we may receive a commission if you click a link and purchase something that we recommended. Read more about Affiliate disclosure here.
And that’s the reason why I and millions of others chose this great DAW for music production.
This is the first part of Ableton tutorial where you get the basic knowledge of this software including the session view, arrangement view, preferences, etc. So, let’s begin
Introduction to Ableton Live Interface
In this section, we will go through six topics,
- What is DAW
- Ableton Live Vs Other DAWs
- Ableton Session View
- Ableton Arrangement View
- How to Use Live Browser
- Preferences
These topics are the backbone of Ableton live recording. However, these are the basic things and if you are familiar with DAW recording you would understand these terms easily.
What is A DAW
A DAW or digital audio workstation is a type of software program which can be used to record, edit, mix, and export digital audio within your computer.
There are several DAW software available in the market but the most commons are Ableton Live, Logic pro x, Cubase, Pro Tools, Logic, GarageBand, Audacity, Reaper, etc.
When you dig deep into the details you will find that each DAW is known for its own unique layout and features, but the main work of a DAW is recording, editing, and processing digital audio.
I’ve used several times here the term “digital audio” because there is another type of recording exists – Analog recording, which produces analog audio signals and obviously different from digital audio.
There is a vast debate under digital and analog audio so I want to skip this topic for today. We just discuss here the features of a DAW. Here are the core features of a DAW
- It is capable of recording multi-track simultaneously. You just need a multichannel input audio interface to record multitrack simultaneously.
- DAWs incorporate MIDI functionality which allows you to program the notes by playing via Midi Controller You can use those notes to produce great music with Virtual Instruments.
- The third and most viable benefit of DAW is plugin support. You can use plugins to shape your mix like pros. Plugins can do everything from a simple compression and EQ to hardware emulations.
These features make a DAW is the best option for home studios. Those who can’t afford costly hardware can produce industry-standard audio with just the right DAW.
I’ve used the term “right DAW” because choosing the wrong DAW could ruin your recording. Don’t go for free available options, always choose a professional one.
Ableton Live is a great option if you want to create quality music from your home studio. If you don’t have a copy of Ableton Live – Save one for you here
Ableton Live Vs Other DAWs
I know you are wondering if there are several professional DAWs in the market then why Ableton? Well here are a number of the advantages of using Ableton over other DAWs.
- State-of-the-art Midi Programming interface – Which makes it a full-featured Midi sequencing giant.
- Ability to play with Midi and Audio clips simultaneously with the help of Live Bowser and the Arrangement View.
- Faster editing – When you will be familiar with this DAW you will notice that it’s much faster the other DAWs in terms of editing.
- Wide Library of Loops and samples
- And the last but not least – The Price. It’s fairly cheaper than other Midi sequencing DAWs like Cubase and Logic Pro X.
I think you are now better convinced about Ableton Live. Now it’s time to jump into Ableton live interface introduction.
Introduction to Ableton Live Interface
there are seven main parts of the Ableton Live interface
- Ableton Session View
- Ableton Arrangement View
- Browser
- Groove Pool
- Info
- Midi Instrument/Sample/Effect Window
In this section, we will take a closer look at these views and know how they are useful in creating music in Ableton.
Ableton Session View
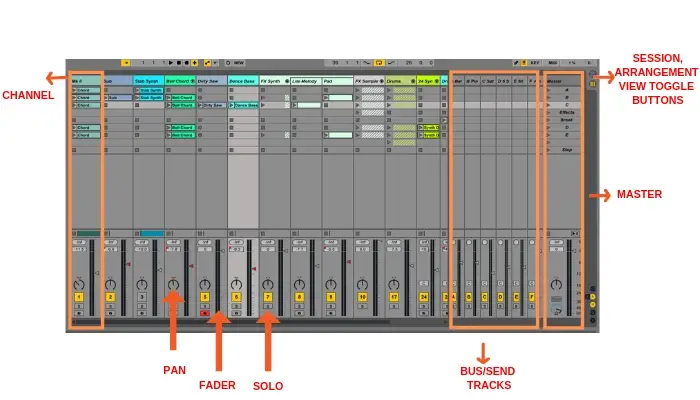
Note: If the session view is not opened in default. You can open it by going to View>Session View or clicking on the Session/Arrangement Window toggle button on the upper right corner as shown in the above image. Session View has many functions which are common in all DAWs.
- Channels
- Pan
- Fader
- Solo/Mute
- Bus, Send/Return
- Master Fader
Channel: In DAWs individual tracks are called channels where you can add effects select input/output, solo/mute, and toggle record enable individually.
Pan: Pan is a feature of the channel which is used to pan the selected track’s sound left and right.
Faders: faders are used to balance the volume for individual channels. Each channel has its own separate fader. There are other faders also like Master fader, Bus, and send faders.
Solo/Mute: Solo and mute buttons are used to listen to channels in solo mode and mute individual tracks respectively.
Bus, Send/Return: these channels are used to add effects like reverb and delay and routing/grouping the instrument and audio tracks.
Master Fader: Master fader is used to balance the master output sound and add effects to the output. All channels whether its individual channel, sends or bus are routed to the master fader.
Ableton Arrangement View
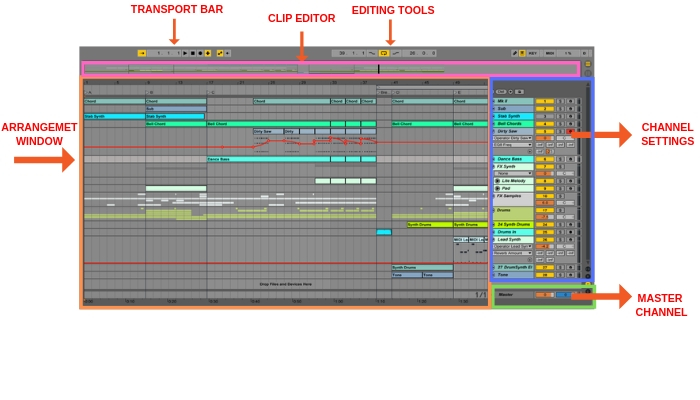
Ableton arrangement view can be accessed in two ways.
- Session/Arrangement toggle buttons located at the upper left corner of the interface
- View menu > Arrangement
The different parts of the arrangement view are shown in the image above. We will go through each part one by one.
Arrangement Window: Arrangement window works as the main editor panel of Ableton lives where we edit the clips with the given editing tools.
Channel Setting: However most of the channel setting tools are available in the session view where we can add effects, pan, volume, select input and outputs for the channels, some settings are also available in the arrangement view. You can use this section to quickly apply settings to the channels without toggling into session view.
Master Channel: The master channel (master fader) is also available in arrangement view.
Transport Bar: It’s available globally which means it’s visible in all the views. You can use the transport bar to play, pause, record, etc.
Editing Tools: Editing tools like cut, paste, glue, etc are available in the editing toolbar located just above the arrangement view.
Clip editor: Clip editor is used to edit the clips individually. You can use it to edit clips with extra precision.
Ableton Live Browser
Ableton is the kind of audio programming software where you can program your music with virtual instruments and samples.
The browser feature is the most important feature in Ableton live which is the gateway to the tons of instruments and samples.
With the browser, you can import pre-made instruments as per your need. In the default installation of Ableton live you will get approx 25GB of virtual instrument and sample library which I think is enough for a home studio.
If the browser is not open in default in your Ableton live window, you can easily open it by pressing “ctrl+alt+B” or going to View>Show Browser to open it.
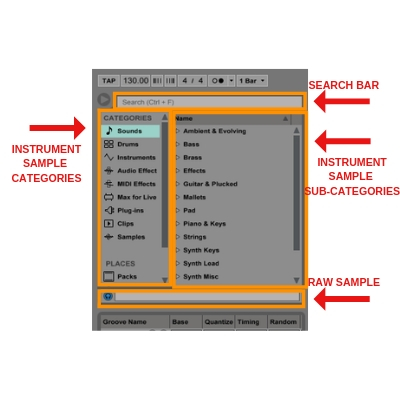
You can locate the browser feature in the upper left section of the session/arrangement view.
How to Use Ableton Live Browser?
At the left side of the browser window, you can see different categories like sounds, drums, instruments, etc.
When you click on your desired category, several subcategories will show on the right side of the window (Name).
Now click on the arrow shown beside the subcategories to access the related sounds, instruments, presets, and other stuff.
When you accessed the desired stuff Select a track or open a new one and just drag that stuff to the Sampler Window.
Note: For Midi instruments, select an existing or new Midi track. For Audio tracks and effects select an audio track.
Groove pool
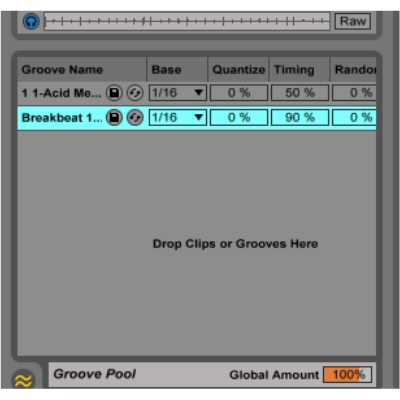
Ableton Groove Pool is located just below the Browser. It is used to import the-made groove (beats) from the browser library to your session. You can also save your own made grooves by just dragging in the clips into the groove pool.
It’s very simple. You just have to drag the desired clip from the arrangement window to the grove editor.
When you drag the clip into the groove pool you will be asked to set the name, base, quantize, and timing of the clip and then you can save this clip to the user library in the browser.
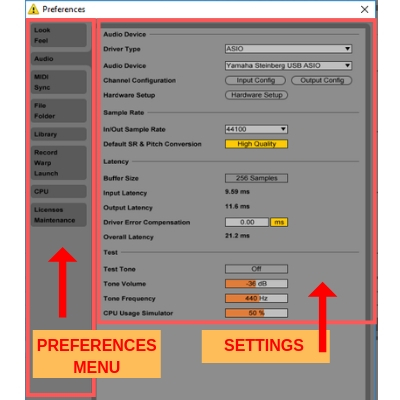
Ableton Live Preferences
Abelton live preferences can be accessed from the Options menu or you can press the “ctrl+,” keyboard shortcut to access the preferences window. Here are the settings that Ableton preferences window provides us.
- Look and feel: This setting is used to change the default look and feel of the Ableton live interface.
- Audio: This option is used to set up the audio interface, latency etc.
- Midi/Sync: This option is used to set up the input output for the Midi instruments and devices.
- File and Folder: It’s used to change the files and folders settings for the clips.
- Library: Here you can set up the folder for the library.
- Record warp launch: this setting is used to warping and launching samples
- CPU: You can setup CPU usage here.
- Licence maintenance: This menu is used to maintain the licence of the software.
Well, here was the short introduction to the award-winning DAW – Ableton live.
In the second part of this tutorial, we will learn about how to work with clips in Ableton Live to make songs.
The second part will contain information about audio and Midi clip editing, warping, importing, and launching clips.
If you want to know more you can refer to the free video course by Noiselab Click here to join this free course Read also,